Abstract
Introduction
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is characterized by chronic hemolysis which is caused by the polymerization of the abnormal sickle hemoglobin (HbS). The ongoing intravascular hemolysis leads to the release of cell-free heme and iron, resulting in widespread oxidative damage, inflammation, neutrophil activation and pro-inflammatory phenotype and endothelial activation, all contributing to vaso-occlusive events and end organ damage. Voxelotor, a small molecule reversibly binding to hemoglobin (Hb) increases its oxygen affinity, thereby decreasing Hb polymerization and sickling, ultimately resulting in improved sickle erythrocyte deformability and decreased hemolysis. The decrease in cell-free heme and labile plasma iron might result in decreased inflammation and neutrophil activation, adhesion and aging.
The aim of this study is to assess the effects of voxelotor on erythrocyte deformability and neutrophil adhesion and aging.
Methods
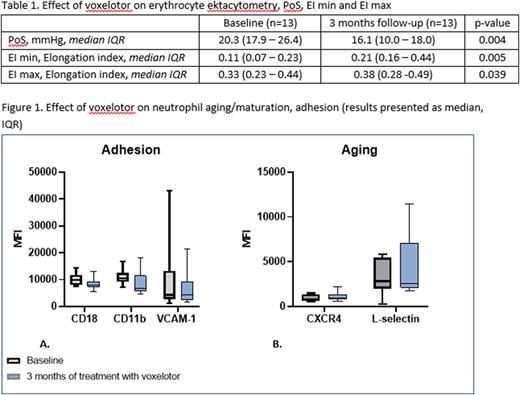
SCD patients with severe genotypes (HbSS and HbSβ0-thalassemia) and hemoglobin levels ≤ 10.5 g/dL were treated with voxelotor 1500 mg in a single arm study at Amsterdam University Medical Centers, The Netherlands. Blood was collected at baseline and after 3 months of treatment. Erythrocyte deformability was assessed by ektacytometry (Lorrca, RR mechatronics, The Netherlands) by measuring elongation index (EI) and point of sickling (PoS). EI max and EI min indicate the highest and lowest erythrocyte deformability upon oxygenation (normoxic conditions) and deoxygenation (hypoxic conditions) respectively. The PoS is the oxygen tension at which 5% reduction of the EI max is observed. Antigen expression of neutrophil markers specific for endothelial adhesion (CD18, CD11b and VCAM-1) and aging (CXCR4 and L-selectin) were assessed with flow cytometry.
Results
Preliminary results of 13 (of a planned study population of 20) SCD patients (HbSS/HbSβ0-thalassemia 9/4, median age 35 years (IQR 28 - 46), 5 female) who completed three month follow-up are described. Hb levels increased significantly after 3 months of treatment (from median 7.4 (IQR 6.9 - 8.0) g/dL to 9.7 (8.1 - 10.8) g/dL, p=0.001), corresponding to significant decreases in LDH (p=0.005), bilirubin (p=0.001) and reticulocyte counts (p=0.016) as markers of hemolysis. PoS was significantly lower at 3 months as compared to baseline (median 16.1 (IQR 10.0 - 18.0) mmHg vs. 20.3 (17.9 - 26.4) mmHg, p=0.04). EI min increased significantly from median 0.11 (IQR 0.07 - 0.23) to 0.21 (0.16 - 0.44), p=0.005, while EI max increased from 0.33 (0.23 - 0.44) to 0.38 (0.28 - 0.49) p = 0.039. (Table 1). Markers of neutrophil adhesion (Cd11b/CD18 and VCAM-1) all showed decreasing trends at 3 months, though the changes are currently (n=10) not statistically significant (Figure 1A). The markers of aging did not change significantly although L-selectin seemed to increase (Figure 1B).
Conclusion Voxelotor significantly decreased PoS and increased EI min and EI max, indicating decreased sickling and improved deformability of sickle erythrocytes. Decreasing trends in adhesion markers of neutrophils might indicate that by inhibiting hemolysis, voxelotor may have an ameliorating effect on neutrophil adhesion. Whether voxelotor may reduce neutrophil adhesion and also reduce neutrophil aging as suggested by the increasing trend in L-selectin expression, needs to be awaited until after completion of the entire study cohort.
Disclosures
Biemond:GBT: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; CSL Behring: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novo Nordisk: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novo Nordisk: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bluebird Bio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Research Funding; Chiesi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Modus Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanquin: Research Funding; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bluebird Bio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Chiesi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CSL Behring: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Research Funding; GBT: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Nur:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal